Articles
DISCOVER
sustainable advancements spanning agricultural to industrial domains. Explore patents and research articles covering precision agriculture, intelligent controls, advanced flow systems, and more.
Patent Publication (2024)

SMART VARIABLE RATE LIQUID FERTILIZER APPLICATOR FOR TREE CROPS
Muhammad Yamin1, 2, Wan Ishak bin Wan Ismail2, Muhamad Saufi bin Mohd Kassim2, Samsuzana Binti Abd Aziz2, 3
- Department of Farm Machinery & Power, Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (38040) Pakistan
- Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
- SMART Farming Technology Research Center, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
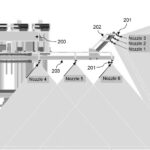
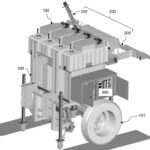
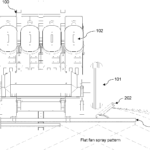
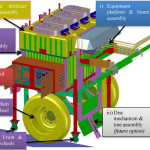
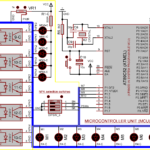
The present invention discloses a smart variable rate liquid fertilizer applicator for a tree crop plant in a plantation. The fertilizer applicator comprises a main body frame (100) having wheels (101), input devices for providing input data including data of macronutrients including nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (NPK) in the soil of the plantation, data of speed of the fertilizer applicator and associated data thereof, a set of output devices in communication with the input devices for preparing a customized NPK blend of liquid fertilizers (i.e. NPK liquid fertilizers at variable rates) to the plantation based on the data of macronutrients and the data of speed, and an applicator wing boom assembly (200) extending laterally from the main body frame (100) towards the crop plant comprising a first boom (202) and a second boom (203) for mounting spray nozzles (201) there along. The spray nozzles (201) are connected to the NPK macronutrients flow control valves at a fertilizer mixing line to dispose the NPK liquid fertilizers at variable rates in a uniform manner to a designated target soil area around the crop plant in the plantation (Figure 1).
Patent No. MY-202945-A
Patent Publication (2023)

SYSTEM OF INTELLIGENT VRT CONTROLLER FOR VARIABLE RATE LIQUID FERTILIZER APPLICATOR AND METHOD THEREOF
Muhammad Yamin1, 2, Wan Ishak bin Wan Ismail2, Muhamad Saufi bin Mohd Kassim2, Samsuzana Binti Abd Aziz2, 3
- Department of Farm Machinery & Power, Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (38040) Pakistan
- Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
- SMART Farming Technology Research Center, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
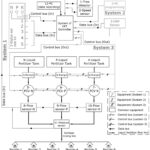
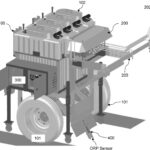
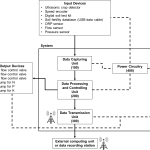
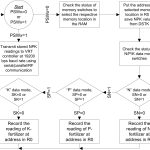
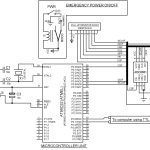
The present invention discloses a system of intelligent VRT controller for regulating application of liquid fertilizers to a crop plant in a plantation using a fertilizer applicator and a method thereof. The system comprises a data capturing unit (100) comprising an analog-to-digital converter for receiving input data including data of macronutrients including nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (NPK) in the soil of the plantation and data of speed of the fertilizer applicator thereof from input devices selected from a group comprising an ultrasonic tree detector, a speed encoder, a digital soil test kit, a soil fertility database, an oxidation reduction potential (ORP) sensor, flow sensors and a pressure sensor; a data processing and controlling unit (200) for analyzing the input data received thereof and determining, based on the data of macronutrients and the data of speed, a nutritional state of the plantation, a NPK macronutrients deficiency score of the plantation and a set of NPK macronutrients flow rates to trigger a set of output devices deployed at the fertilizer applicator for disposing a customized NPK blend of the liquid fertilizers (i.e. NPK liquid fertilizers at variable rates), wherein the set of output devices comprises NPK macronutrients flow control valves including a nitrogen flow control valve, a phosphorus flow control valve and a potassium flow control valve; and a data transmission unit (300) for transmitting the input data received thereof, the data of macronutrients, the data of speed, the nutritional state of the plantation, the NPK macronutrients deficiency score, and the set of NPK macronutrients flow rates to an external computing unit or data recording station (Figure 1).
Patent No. MY-197872-A
Research Article (2022)

DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS OF VARIABLE RATE LIQUID FERTILIZER APPLICATOR FOR MATURE OIL PALM TREES
Muhammad Yamin1, 2, Wan Ishak bin Wan Ismail2, Samsuzana Binti Abd Aziz2, 3, Muhamad Saufi bin Mohd Kassim2, Farah Naz Akbar4, Muhammad Ibrahim5
- Department of Farm Machinery & Power, Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (38040) Pakistan
- Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
- SMART Farming Technology Research Center, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
- Department of Allied Health Sciences, Sargodha Medical College, University of Sargodha (40100) Pakistan
- Department of Environmental Sciences & Engineering, Government College University Faisalabad (38000) Pakistan
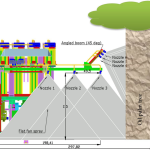
This research study focuses on the design of variable rate liquid fertilizer applicator which can measure the NPK status of soil and applies N, P and K nutrients simultaneously at separate variable rates around the oil palm trees in the form of aqueous solutions of straight fertilizers having single nutrient. A fertilizer flow control and spray system was designed to apply liquid fertilizer around the oil palm tree on a 5 m × 5 m (25 m2) area of most effective roots. On the basis of simulation and calculations, six 8006 flat fan nozzles were selected to maintain the adequate swath coverage of fertilizer spray. The nozzles 1-3 were mounted vertically on the horizontal boom to spray on the machine side of an oil palm tree, i.e. the side of an oil palm where the machine is passing through. Whereas nozzles 4-6 were fixed at -22°, -21° and -20° angles with respect to the horizontal plane on a 45° angled boom to spray across the tree using trajectory method. An average simulated liquid velocity of 14.05 m/s from each nozzle was found to spray at 2.5 m distance across the tree using trajectory method. Thus an improved distribution of fertilizer around the tree at 25 m2 area of most effective roots can be achieved using this system. Mechanical structure of the applicator which carries all the equipment and fertilizer tanks was designed by using the finite element analysis. Minimum safety factors of 3.13 and 11.34 were found for mechanical structure and fertilizer tank assembly respectively which were satisfactory to bear the necessary loads during field operation.
Research Article (2021)

DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT) BASED AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING THE ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN TUNNEL FARMING
Muhammad Yamin1, Usama Ali Zafar1, Ghulam Usman2, Muhammad Nauman1, Muhammad Rizwan3, Muhammad Nadeem1, Muhammad Azhar Ali1, Usman Haider1
- Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, 38000, Pakistan
- Water Management Training Institute, Lahore, 38000, Pakistan
- Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
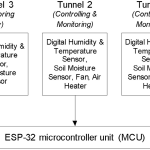
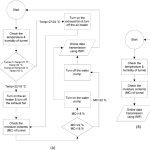
Tunnel farming is getting popularity among the farmer’s community of Pakistan due to the possibility of growing off-season vegetable crops with high yield in controlled environment. In current study, the development and validation of IoT system consisting of monitoring and control units was carried out for controlling the environmental factors in tunnel farming. Three tunnels were set for monitoring the environmental factors using temperature, humidity and soil moisture sensors. Two of three tunnels were fit with control units of exhaust fans and air heaters and a water pump for controlling the temperature and soil moisture. During the testing and validation of system, temperatures recorded through DHT-21 sensor and thermometer in tunnel 1, 2 and 3 had strong correlations of 0.9986, 0.998 and 0.9978 respectively. Similarly, strong correlations of 0.9987, 0.9994 and 0.998 were found for RH (%) measured through DHT-21 sensor and RH meter for tunnel 1, 2 and 3 respectively. Similarly, strong correlations of 0.9987, 0.9994 and 0.998 were found for RH (%) measured through DHT-21 sensor and RH meter for tunnel 1, 2 and 3 respectively. For soil moisture measurement, similar correlations were observed for resistive soil moisture sensor and oven dry method. It was explored that an increase in temperature through air heater decreases the RH in tunnel 1 and 2 compared to the tunnel 3 which has higher RH because it was not installed with air heater and exhaust fan. System controlled the temperature and soil moisture within adjusted limits of 22-27 °C, 17-23 % for tunnel 1 and 19-22 °C, and 19-23 % for tunnel 2.
Research Article (2020)

MODIFICATION OF COLORIMETRIC METHOD BASED DIGITAL SOIL TEST KIT FOR DETERMINATION OF MACRONUTRIENTS IN OIL PALM PLANTATION
Muhammad Yamin1,2, Wan Ishak bin Wan Ismail2, Muhamad Saufi bin Mohd Kassim2, Samsuzana Binti Abd Aziz2, Farah Naz Akbar3, Redmond R. Shamshiri4, Muhammad Ibrahim5, Benjamin Mahns4
- Department of Farm Machinery & Power, Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (38040) Pakistan
- Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
- Department of Allied Health Sciences, Sargodha Medical College, University of Sargodha (40100) Pakistan
- Leibniz Institute for Agricultural Engineering and Bioeconomy, Max-Eyth-Allee 100, 14469 Potsdam-Bornim, Germany
- Department of Environmental Sciences & Engineering, Government College University Faisalabad (38000) Pakistan
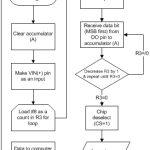
It is the need of time that oil palm farmers must perform the spatially planned soil analysis to know about the fertilizer sufficient and deficient zones of land. Colorimetric method is a suitable and fast solution of soil analysis for NPK determination using the digital soil test kit. NPK determination procedure with a digital soil test kit was undefined for oil palm. Furthermore, the digital soil test kit determines the passage of light through an opaque medium of soil solution with a specified reagent. Therefore, environmental light may interfere leading to wrong results of NPK measurement. Likewise, this equipment was non-incorporable with the controller of any VRT fertilizer applicator. In this research, these issues were addressed and the NPK measurement procedure was defined for oil palm plantation by modifying the ‘soil to water’ ratio in sample soil solution with an optimum environmental light range of 18-23 W/m2. ‘Soil to water’ ratios were found for nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium as 0.31 to 5, 1 to 5 and 4.5 to 5, respectively to fit the requirement of NPK for oil palm in the prescribed range of the equipment. Validation study of modified digital soil test kit showed that 91.7% N, 89.6% P and 93.8% K results of modified digital soil test kit were matched with analytical laboratory method. Thus the reliability of NPK results using digital soil test kit was enhanced, making the kit incorporable with the controller of variable rate fertilizer applicator through remote monitoring based data acquisition system. The outcome of this research can be used in the development of an IoT network data fusion for dynamic assessment of the NPK variation in the soil and nutrient management in oil palm plantations.
Research Article (2020)

DEVELOPMENT AND CALIBRATION OF ORP SENSOR FOR THE ESTIMATION OF MACRONUTRIENTS IN THE SOIL OF OIL PALM PLANTATION
Muhammad Yamin1,2, Wan Ishak bin Wan Ismail2, Muhamad Saufi bin Mohd Kassim2, Samsuzana Binti Abd Aziz2, Ramin Shamshiri3, Farah Naz Akbar4, Muhammad Ibrahim5
- Department of Farm Machinery & Power, Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (38040) Pakistan.
- Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
- Leibniz Institute for Agricultural Engineering & Bioeconomy, 14469, Germany.
- Department of AHS, Sargodha Medical College, University of Sargodha (40100), Pakistan.
- Department of Environmental Sciences & Engineering, Government College University Faisalabad (38000) Pakistan.
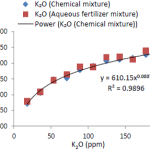
To practice the concept of site specific crop nutrient management on a large oil palm plantation, more soil samples are required to analyze the macronutrients. Most of the farmers in developing countries cannot afford the high cost of soil analysis. If fertilizers are applied by maintaining the desired NPK ratio in soil for a long time, then maintained ratio of NPK in the soil can help to estimate the deficiencies of NPK nutrients in the soil using oxidation-reduction potential. In this study, oxidation-reduction potential was recorded in chemical (NO3–, H3PO4, K+) and aqueous fertilizer (NO3–, TSP, MOP) mixtures separately with the help of developed ORP sensor and commercially available ORP meter (HM ORP-200). The calibration of developed ORP sensor in different concentrations of chemical (NO3–, H3PO4, K+) mixture has a good correlation of 0.9923 with validation readings recorded in corresponding aqueous fertilizer (NO3–, TSP, MOP) mixtures with an error range of -0.44 to 1.72 %. This small error range reveals that ORP sensor calibrated in chemical (NO3–, H3PO4, K+) mixture of NPK nutrients can be used reliably in aqueous fertilizer (NO3–, TSP, MOP) mixture for the estimation of NPK nutrients. A good correlation of 0.9766 was also found between ORP sensor and commercially available ORP meter (HM ORP-200). Developed ORP sensor can be used for on-the-go operations in the soils of oil palm plantations because of its fast response time (<1 s) and notably high oxidation-reduction potential provided that required NPK ratios are maintained in the soil.
Research Article (2018)

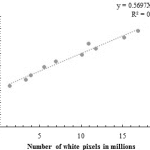
WATER QUANTIFICATION FROM SPRAYER NOZZLE BY USING PARTICLE IMAGE VELOCIMETRY (PIV) VERSUS IMAGING PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
Muhammad Nadeem1, Young Ki Chang2, Uday Venkatadri1, Claver Diallo1, Peter Havard2, Tri Nguyen-Quang2
- Department of Industrial Engineering, Dalhousie University, PO BOX 15000, Halifax, NS, B3H 4R2, Canada
- Department of Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture, Dalhousie University, Truro, Nova Scotia, B2N 5E3, Canada
Distribution of agro-chemicals through sprayer nozzles is very important because there is a significant loss of agro-chemicals such as pesticides during spraying due to non-uniformity of droplet and off-target drift. Improving the efficiency of spray pattern would reduce energy, costs and also minimize environmental pollution. In this paper, we examine jet patterns to study the performance of water distribution during the spraying process. We present a method to quantify water amount from a sprayer jet by using Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) system in combination with imaging processing. For this study, ten sets of images were acquired with a PIV system in double frame mode. Each set of images contained different numbers of double-framed images: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 and 100 at eight different pressures 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 175 and 200 kPa. The PIV images obtained were analysed using an image processing software for droplets and volume calculations. The results showed good agreement of both manual and PIV measurements and suggested that the PIV coupled with image processing technique can be used for a precise quantification of flow through sprayer nozzles.