Autonomous Vehicles in Precision Agriculture
Muhammad Nauman, Muhammad Yamin, Abdul Ghafoor
Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
Modern agriculture is devised with automation, which has revolutionized conventional farming and enhanced crop productivity, quality, irrigation efficiency, economy and made it energy efficient by saving the energy cost up to 3.2% (agrEE). Automation played a promising role in the promotion of precision agriculture with the use of data driven decision support systems. Autonomous farming reduces manual labor, while increasing capacity of precision farming by precise land preparation, seeding, planting, chemical applications, and harvesting. The use of autonomous vehicles has made it possible to enhance farming efficiencies by 15% (Trimble), with the use of wide range of precision agricultural technologies and real-time data-driven machines, which are not constrained by time of day or weather.
In precision agriculture autonomous vehicles are used for various farming operations such as:
Land Leveling
To enhance irrigation efficiency, precision land leveling with autonomous tractor is a precision operation for seed bed preparation.
Precision land leveling requires very high precision for basin irrigation as well as for furrow and border irrigation, which can be achieved using GPS guided or laser land leveler. To achieve required slope of land with precision the vehicle multiple times run over the field and causes compaction. GPS guided leveler this effect by guiding the right location to the operator where it is needed, while manually operated conventional laser leveler run over the entire field. The operation of laser land leveling with autonomous vehicle can reduce the overrunning the field by gathering real time data and avoiding the piece of land, which is already been leveled, hence improving leveling efficiency, economy, and sustainability of the soil.
Sowing/Planting
Precision sowing and planting has already been in practice in different areas of the world with different of precision. The important parameters which are taken into consideration for sowing of the seeds are:
i. Depth of seed
ii. Seed to seed distance
iii. Row to row distance
iv. Number of seed per hill
v. Forward speed of the vehicle
Speed of the seeding vehicle directly influences the seed rate, as it is needed to be placed at measured distance for precision. Variation in speed causes undulations which can variate above stated parameters and reduces precision level. Maintaining the number of lines sown per unit area and line to line distance is essential as it ensures the required plant population, yield and allows other operations i.e. spraying, fertigation, weeding, and harvesting, to perform with ease. It has been observed that, during seeding operation after each turn at the end of field the operator cannot maintain the line to line distance. Even the variation of an inch at every turn can add or skip complete line(s) leading toward poor precision and other operation. Map based or GPS guided autonomous vehicles can resolve speed fluctuation problem and maintain line to line distance after each turn, which can enhance productivity.

Spraying and Weeding
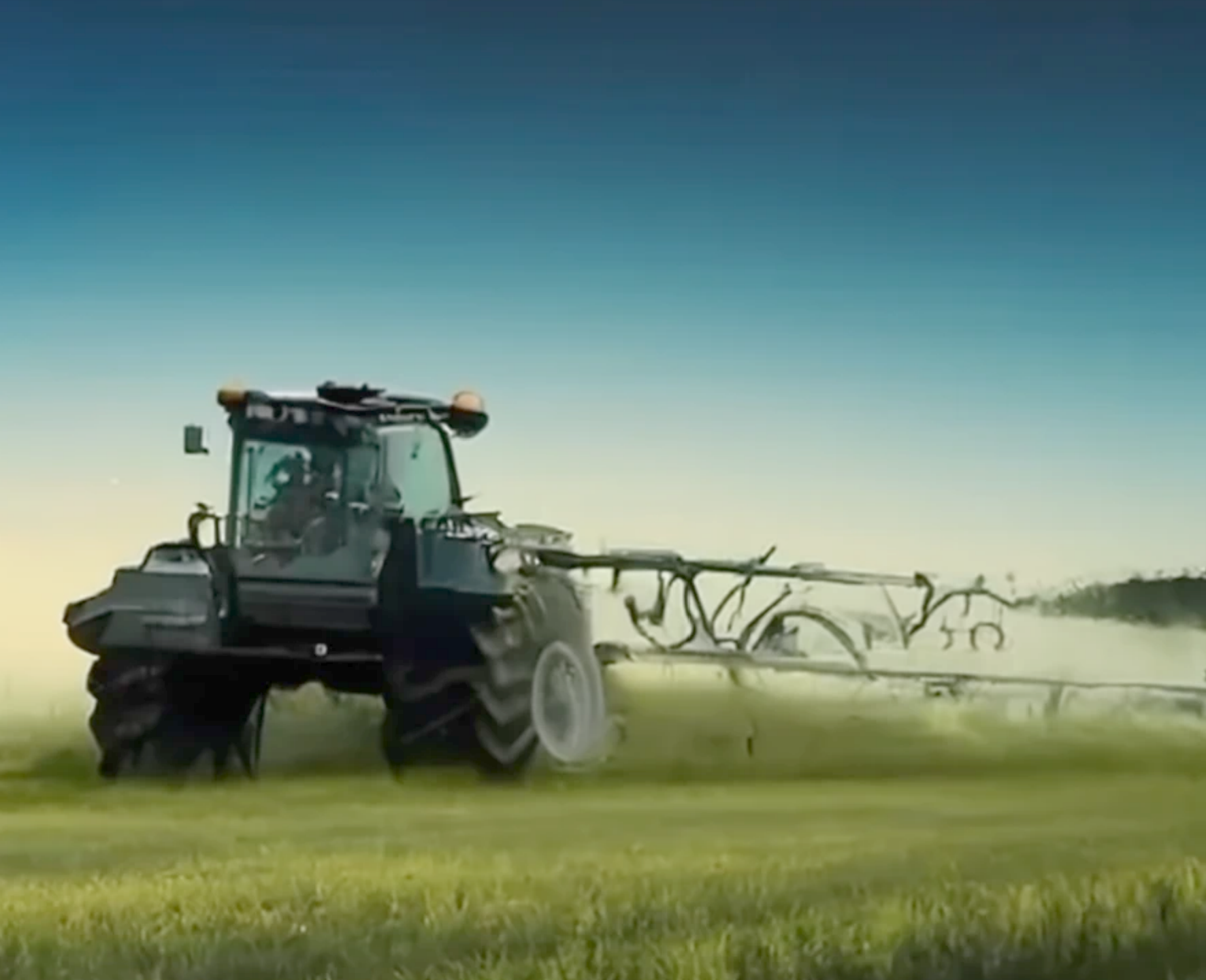
Precision plant protection is needed to improve the environmental sustainability and the quality of produce. Chemical application is in common practice to control insect, pest, disease, weeds and for micronutrients. During spray application forward speed of the vehicle, air and direction must be taken care of to avoid drift of the spray particles and right manner i.e. spray swath, overlap and distance of nozzle from canopy. By the introduction of agricultural spraying drones, efficacy of application has been achieved by saving time, labor, and energy. A 2023 study referenced by Times of Malta highlights the potential of drone-assisted crop monitoring to significantly reduce pesticide use by up to 15%. This is achieved through targeted application, minimizing waste and environmental impact.

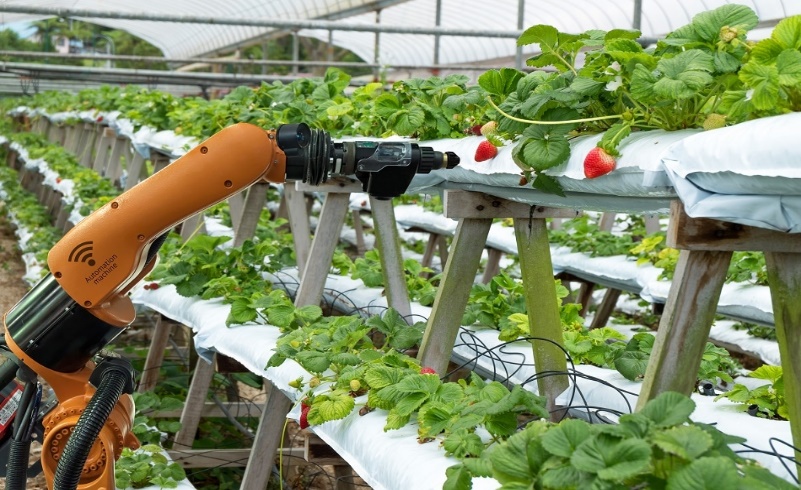
AI based robotic mechanical weeder reduces the application of weedicides at early stages of crops, which leads toward better environmental health. However, orchards required high pressure sprayers to penetrate chemicals into the depth of large canopies, for these conventional small drones are not applicable. Mostly, orchards are being sprayed with tractor mounted/trailed, high pressure, high flow, direct/air assisted sprayers. Precision orchard sprayer operated with autonomous tractor can enhance the efficacy of spraying application by maintaining optimum speed at different wind conditions and by covering complete periphery of canopies.
Combine Harvesting
Modern combine harvesters are equipped with about a dozen sensors and cameras at different locations to monitor throughput capacities at feed intake, output, grain pan, sieves, straw walkers, moisture content, grain quality, grain content, threshing rate, concave clearances, drum speed, reel index, cutting index, sieve vibration, inclination, cleaning, and overall mass flow rate. Autonomous combine harvesters boast two key advantages: they can operate continuously, significantly outperforming human workers in efficiency (up to 30%), and they achieve the lowest possible harvest losses, minimizing waste to a mere 2% (Future Farming).

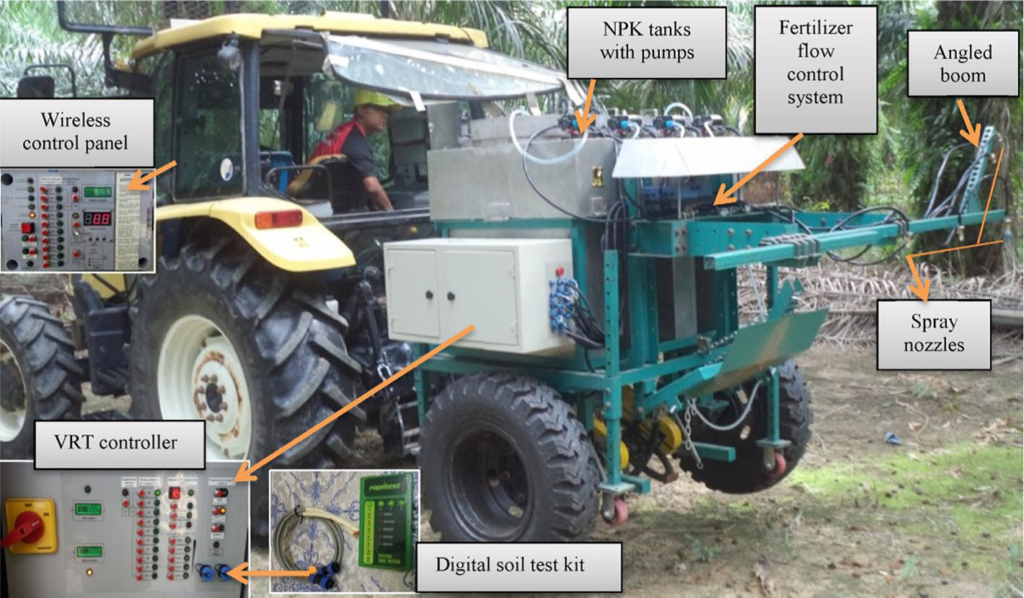
Soil Nutrient and pH Management
Uniform application of soil nutrients and pH stabilizers are being applied conventionally which causes nutrient over and deficient soil, unmanaged patches of land with poor pH value. This practice reduces soil health, sustainability, productivity and also pollutes its environment. Autonomous real time nutrient and pH manager can apply site specific ingredients, increasing the productivity of the soil.

Conclusion
The integration of autonomous vehicles in precision agriculture marks a significant leap forward in modern farming practices. These vehicles, ranging from advanced tractors to precision sprayers and harvesters, are revolutionizing every aspect of the agricultural workflow. By harnessing the power of data-driven decision support systems and real-time monitoring, autonomous vehicles optimize land preparation, seeding, planting, chemical applications, and harvesting processes. Through precise operations, they enhance irrigation efficiency, minimize resource wastage, and maximize crop yields. Moreover, the deployment of autonomous vehicles addresses critical challenges such as labor shortages and environmental concerns, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient agricultural sector. As we continue to embrace autonomous technologies, the future of farming looks brighter than ever, ensuring food security for generations to come.