VRT Fertilizer Applicators
Muhammad Yamin
Faculty of Agricultural Engineering & Technology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
In the past 20 years, the use of agricultural chemicals, including fertilizers, has grown by 78% globally for boosting up the agricultural production according to the FAO. The total fertilizer nutrient consumption was estimated at 205 million tonnes in 2023. Although, fertilizers play an important role for the productive growth of crops in terms of the higher yields but applying them at uniform rates can lead to a 25% increase in soil nitrate leaching, polluting groundwater (source: Environmental Protection Agency). According to the World Bank in 2020, agriculture accounted for 80% of global water pollution. This environmental pollution may not be eliminated completely because of the growing food demands day by day at an exceptional high rate but may be reduced by employing the variable rate technologies (VRT) for the application of fertilizers leading towards more profit and less environmental pollution.
At the time, variable rate technology is the only way which helps to improve the input application efficiency by applying the fertilizer at optimum or near optimum rates according to the soil and crop conditions. Therefore, it is a very important segment of precision agriculture. The popularity of variable rate technology is growing because economic and environmental demands are causing the agricultural production sector to pursue the more economical and environmental friendly ways of producing food. With the development and availability of computer, sensors, control valves, actuators, GPS receivers and better data acquisition systems; VRT has a potential to improve the productivity and profitability while providing the protection to our natural and agricultural resources. Studies have shown that VRT can help farmers save an average of 11.9% (~12%) on fertilizer costs while also increasing crop yields by 5-10%.
Types of Variable Rate Technology
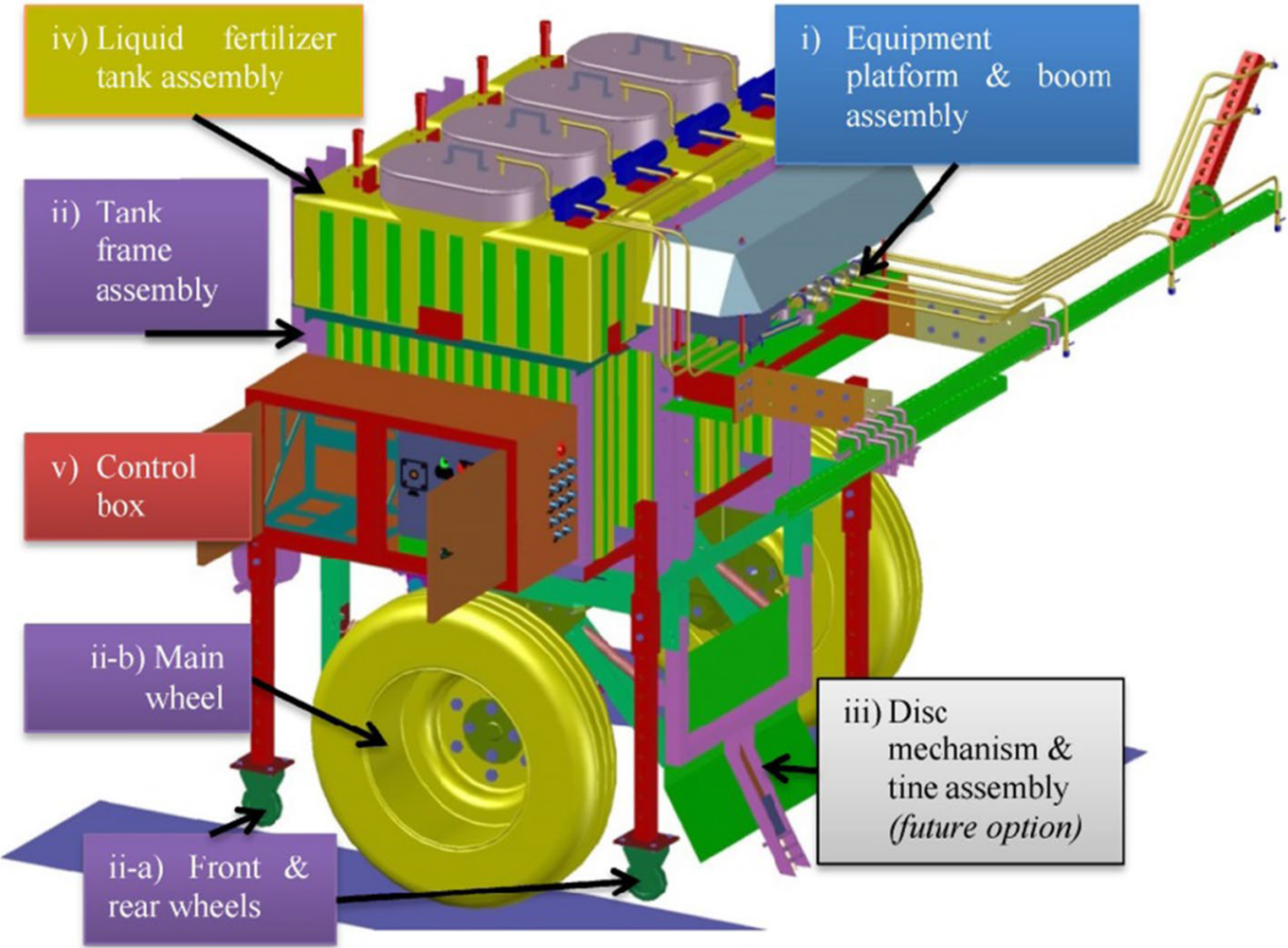
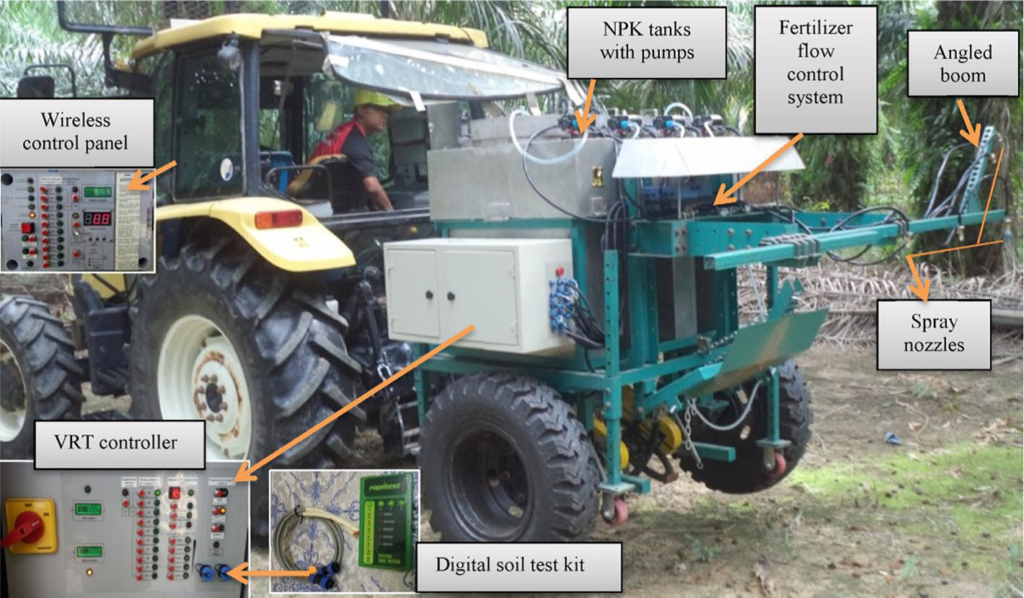
Variable rate technology (VRT) can be categorized in three basic groups; map based VRT, real time sensor or vision based VRT and hybrid VRT which is the combination of first two types. Map based VRT is used when variability of macronutrients in the soil is already available. Many researchers used map based VRT fertilizer applicators which are dependent on nutrient prescription maps. Laboratory data of nutrients are used to prepare the prescription maps which takes long time (≥ 3 weeks) because it involves the analysis of soil sample. During the long time, nutrient scenario in the field may change due to the surface run off in rain fed areas. Thus, long time of nutrient analysis is a big issue along with the cost of soil analysis because commercial laboratories charge high amount ($20 to $50) for a single soil sample depending on the laboratory and the number of nutrients tested. Many studies have indicated a considerable variability of macronutrients in small areas. Therefore, cost of soil analysis may increase considerably depending upon the resolution of field.
On the other hand, real time sensor based VRT does not need extra systems and time to prepare the prescription maps. This technology uses the sensors or equipment to detect the required soil or plant information and applies the fertilizer at desired rates. Some researchers used NIRS based VRT fertilizer applicators for nitrogen application but it is an expensive technology and needs site specific calibration. Some other sensors called Ion Selective Electrodes (ISE) have good accuracy up to 95% to analyze the soil fast and accurate but some hindrances prevent the farmers from using the ISE method; one, costly equipment and secondly, there are ISE commercially available for N and K but not for P. ISE sensors also need a considerable development to be used in real time sensing of soil nutrients.
The Economic Benefits of VRT
Beyond environmental advantages, VRT offers significant economic benefits for farmers:
Reduced Fertilizer Costs: By applying fertilizers only where they are needed and in optimal quantities, VRT helps farmers save on fertilizer expenses, which can be a major cost factor in agricultural production. According to a study published in International Journal of Agriculture, Forestry and Plantation, it was found that VRT adoption resulted in an average fertilizer cost saving of ~12%.
Improved Crop Yields: Precise fertilizer application based on specific soil and crop requirements can lead to increased yields by 5-10%, maximizing the return on investment in land, seeds, and other inputs.
Enhanced Farm Profitability: The combined benefits of reduced costs and potentially higher yields contribute to improved farm profitability, making VRT a valuable tool for sustainable farm management.
These economic advantages, coupled with the environmental benefits of minimizing pollution, strengthen the case for wider adoption of VRT in agricultural practices. As VRT technology continues to evolve and becomes more accessible, its potential to contribute to economic and environmental sustainability in the agricultural sector is likely to increase significantly.





Very beneficial for the farmers.
Need of the time to save input cost and enhance the crop yield.
Advanced form that can give help to the farmers.
That’s great innovation 👏 Chaging the future.
Wonderful information, great effort by Dr. Yamin sb
Need of the time to save input cost and enhance the crop yield and great innovation Chaging the future.